In brief
- From the continued evolution of Al-driven chatbots and personalized customer experiences to enhanced security and efficiency, technology is reshaping the core operations of banks and the financial industry itself
- For the five key tech-trending areas, generative AI is cited as one of the most important and transformative technologies for 2024, which could bring many benefits and a keener competitive edge, though banks utilizing it must take extra care
- For years, fintechs and small banks have grabbed the innovation headlines. Now, with quantum computing on the horizon, major banks with larger innovation budgets and strong risk frameworks are fighting back
Hindsight is a wonderful thing.
Not half as wonderful as foresight, though. As the man said (and he should know), “Price is what you pay. Value is what you get”. In other words, investment in your commercial and technological future is worth every penny and more.
In this look at 2024’s onrushing tech juggernaut, we’ll uncover the trends, strategies and technologies that separate industry leaders from followers and help steer your bank toward a prosperous and competitive future. From the continued evolution of Al-driven chatbots and personalized customer experiences to enhanced security and efficiency, we’ll look at how technology is reshaping the core operations of banks and the financial industry itself.
Looking ahead
Data is the new currency. Consequently, cybersecurity and safeguarding customer information will remain front of mind as banks battle increasingly sophisticated threats.
The combined force of data analytics and generative Al is revolutionizing risk assessment, fraud detection and omnichannel transactions. With its ability to generate predictive models and unearth valuable insights buried in vast datasets, AI and advanced analytics will empower decision-makers to make even better, real-time choices.
Take care of your customers
Elsewhere, machine learning (ML) is establishing hyper-personalization and targeting as core services. With ML, banks see customers as individuals, offering them tailored financial products and recommendations, and increasing user satisfaction and loyalty.
Automation — the watchword for efficiency — streamlines manual and other routine tasks, from transaction processing to customer support, freeing human resources for more strategic activities that require creativity and empathy.
Putting down a marker
Embracing emerging technologies enables banks to do more than simply survive. And Zoreza Global can help you thrive in financial markets where agility, insight and innovation are table stakes.
It’s your future. Make the most of it.
Banking market overview
The banking and capital markets industry will face shifting market dynamics, and fundamental and disruptive business model challenges.
As customers become more open to having their banking requirements provided by non-financial institutions, the pace and intensity of competition against new and traditional rivals will rocket.
Key technology trends for 2024
1. Customer engagement and experience
2. Open banking and ecosystem
3. Cards and payments
4. Product and capability innovation
5. Emerging technology
- Generative AI is acknowledged to be one of the most important and transformative technologies for 2024. The technology brings many benefits and a sharper competitive edge, but banks must be careful when using it.
- The banking BPS market is expected to reach $9.5 billion–$9.7 billion in 2024
- Celent expects IT spending to reach $274.4 billion, an increase of 5.0% on 2023
- Over 80% of institutions increased IT budgets in 2023, and 85% are planning increases for 2024
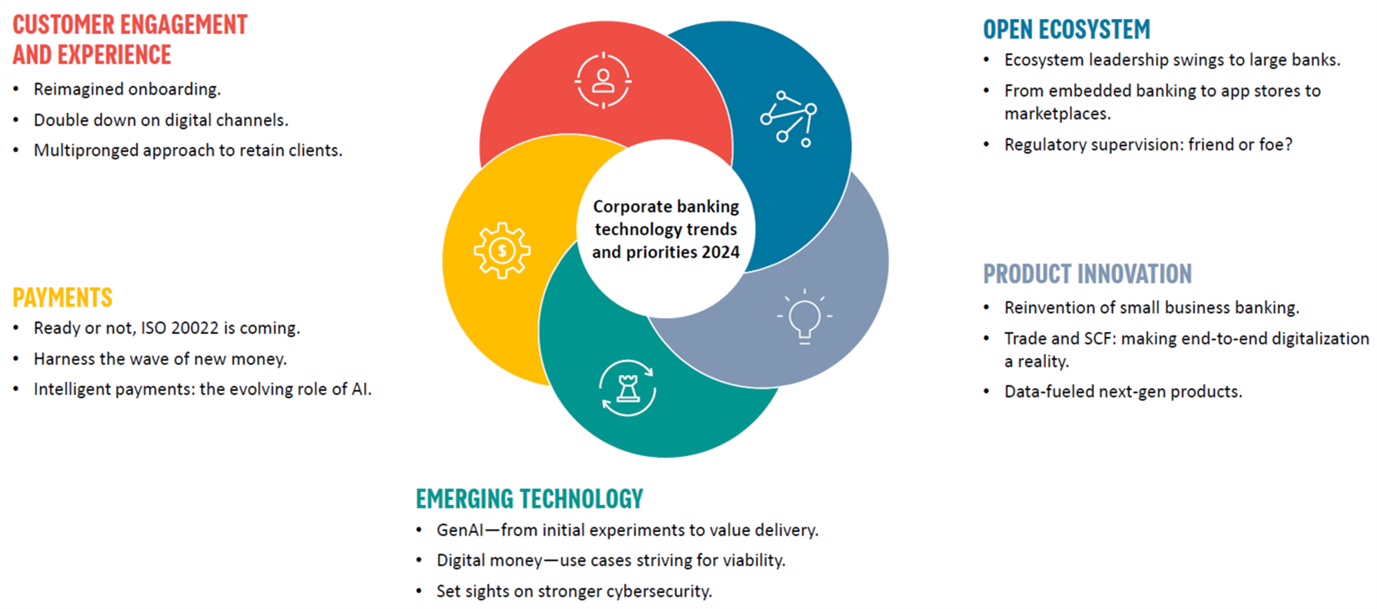
Corporate banking technology trends
|
Corporate banking 2024: Key stats |
|
|
70% |
of banks say, "It’s more challenging to win and retain customers than it was 12 months ago" |
|
52% |
of banks say, "greater speed and agility" is a top priority for solution delivery |
|
83% |
of banks rank "corporate digital channels and trade services/SCF" as top investment priorities |
|
61% |
of banks prioritized advanced analytics, AI and ML as top priorities |
|
5.6% |
The global average by which banks expect their IT budgets to increase in 2024 |
Source: Celent - Technology Trends Previsory Corporate Banking 2024
Prime technology trends for corporate banking 2024
Source: Celent - Technology Trends Previsory Corporate Banking 2024
Customer engagement and experience
- Enhanced onboarding will accelerate in 2024. A digital onboarding experience cuts time-to-revenue and drives the adoption of digital channels from the outset. One bank reimagined its corporate onboarding with a concept of “moments that matter” to clients and the relationship/servicing teams
- Digital channel investments focus on the digital experience or “the consumerization of corporate banking,” including alternative access methods, personalization and embedded servicing capabilities
- Banks will also use digital tools and analytics to enrich client engagement. While modernizing CRM platforms, banks should consider the following as a connected strategy supported by an integrated data and analytics platform:
- Digitally engaged relationship managers
- Beyond CRM — relationship analytics and advisory
- Intelligent contact center
Open banking and ecosystem
- Whether via open banking, embedded finance or banking as-a-Service (BaaS), 75% of banks worldwide said they have a clear engagement strategy for the open ecosystem. Fintechs and small banks entering the BaaS and embedded finance markets have grabbed the innovation headlines for years. Now, major banks with larger innovation budgets and robust risk frameworks are fighting back
- Banks offering banking as-a-Service for digital B2B markets and platforms (allowing the buying and selling of products for multiple vendors) will enable a marketplace to leverage a bank’s license and secure payments network to incorporate financial services into their offerings
- U.S. regulators have established supervisory programs for the safe development of banking innovation and fintech partnerships. Banks must adopt strong risk frameworks with partners and proactively engage regulators where necessary
Cards and payments
- Banks face challenges on multiple payment fronts — compliance programs, rising costs and revenue pressure, etc. — as well as opportunities to differentiate. Making meaningful rather than incremental improvements will be vital
- ISO 20022 is the future, with financial messaging projects in virtually every payment type and country. Banks must implement changes ASAP to derive the full benefit for themselves and their clients
- AI applications are deployed throughout the payment life cycle. Banks must clarify the beneficiary (bank or client) to avoid conflicts of interest
- Innovation will flourish with new forms of money that banks need to rationalize rapidly, establishing which provide client value and how to incorporate them into client propositions
Product and capability innovation
- Bank and third-party small-business banking data can deliver actionable insights to customers and accelerate employees as trusted advisors. Efficient journeys mean focusing on customer-centric workflows across the supply chain, i.e., beyond traditional banking. It also means facilitating financial management by delivering basic alerts, insights and so on
- Trade services: In 2023, the market dynamic changed for banks and corporate clients looking to maximize liquidity and reduce credit exposure. The global supply chain problems increased inefficiency. Banks face an ever-changing technology landscape as fintechs and pioneering banks develop new value propositions and services
- Bank clients want enhanced data-oriented capabilities to improve treasury operations and working capital. Cash management data will be transformed, acknowledging that the underlying data enables a more advisory treasury relationship
Emerging technology
- Generative AI is now a consumer service. What started as a global stateless currency has evolved into routine use cases. With quantum on the horizon, it’s good to begin preparing, if only for cybersecurity reasons
- Early GenAI-mover banks are already progressing from exploration to PoC. GenAI will allow users to combine AI with human intelligence to enhance and expand our abilities — at base level, to generate content and get answers quickly; at a higher level, to improve decision-making, problem-solving and overall cognitive skills. However, it must be handled with care and guidance
- The private sector is ahead of central banks in developing and launching digital money. With proven value in select use cases, initiatives must scale. Only a few central banks have launched CBDCs (to a lukewarm response)
- Corporate bankers and tech partners should initiate a quantum computing program of awareness and understanding
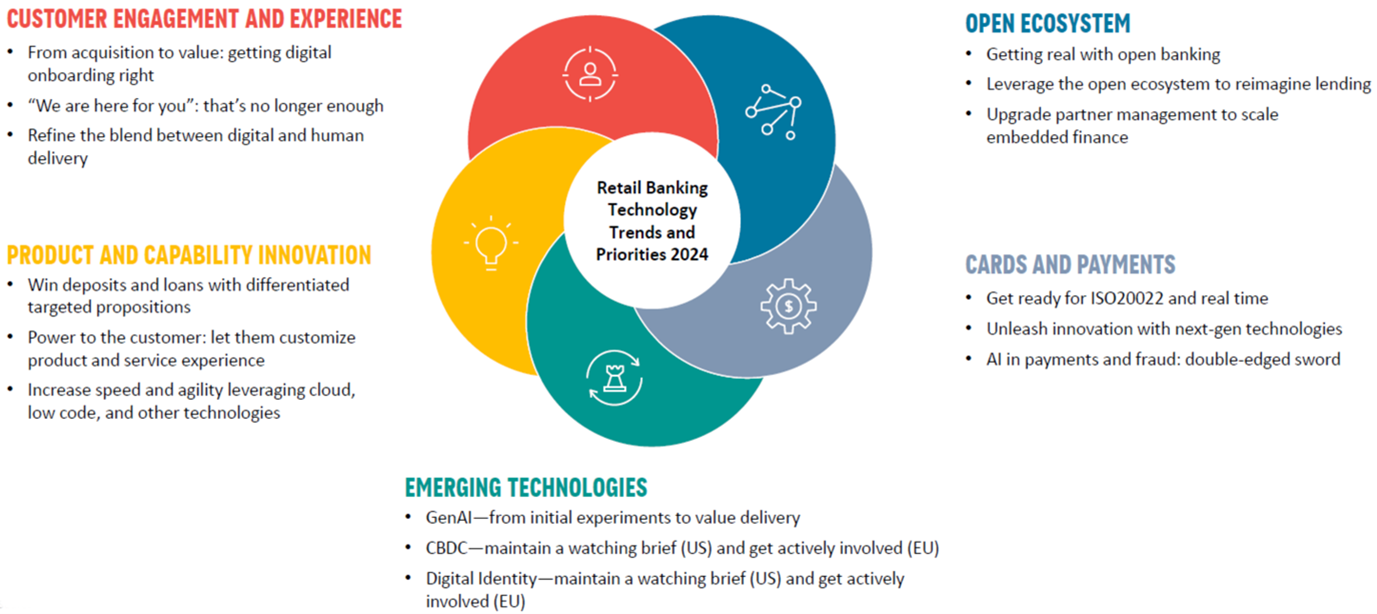
Retail banking technology trends
|
Retail banking 2024: Key stats |
|
|
75% |
of banks say, "It’s more challenging to win and retain customers than it was 12 months ago" |
|
57% |
of banks say, "greater speed and agility" is a top priority for solution delivery |
|
45% |
of banks say, "digital account opening" is a top product investment priority |
|
41% |
of banks are currently exploring GenAI use cases. A further 31% have products related to the technology on their 2023-2024 roadmap |
|
4.6% |
The global average by which banks expect their IT budgets to increase in 2024 |
Source: Celent - Technology Trends Previsory Corporate Banking 2024
Prime technology trends for retail banking 2024
Source: Celent - Technology Trends Previsory Corporate Banking 2024
Customer engagement and experience
- The next evolution of retail delivery will be in hyper-personalized, valuable life and financial experiences for customers. The future is customer engagement
- The difference is a shift from one-time value (“I have an auto loan at a great rate”) to continuing customer value via personalized, proactive digital engagement
- Banks are digitally acquiring new customers. Better onboarding is next up
- “We’re here for you” is no longer enough. Banks must deliver personalized value propositions through ongoing customer engagement
- Banks have overplayed digital’s ability to cut cost-to-serve, treating human-to-human interactions as a last resort. A more balanced model, tailored to each institution’s target market and brand promise, is needed
- Blended automated digital and human assistance will achieve cost savings and retention. GenAI real-time coaching during interactions will help
Open banking and ecosystem
- Three-quarters of banks say they have a clear strategy for increasing open-ecosystem investment, and 60% are generating commercial gains in open finance, BaaS and embedded finance
- The industry agreed on the need for regulatory involvement in innovation. API standards fragmentation, differences in the data banks provide to common requests and inconsistent UX are not conducive to widespread adoption. It also recognized the need for better value-chain cost and incentive alignment
- Lending, a key use case for open banking, gives access to new forms of support application and underwriting process insight. It’s part of a more extensive alternative data landscape for consumer-permission data
- Embedded finance needs fresh thinking, particularly partnerships between banks and fintechs (challenging for both sides). Banks must improve partner relationship management — especially compliance and risk — and explore solutions to help scale embedded finance
Cards and payments
- The impact of activities will not be the same across the board, and not everything needs urgent attention
- Payments remain mission-critical, but banks face many challenges, e.g., compliance programs, rising costs and revenue pressure. Making meaningful rather than incremental improvements will be vital
- ISO 20022 is the future. Banks need to embrace the change in financial messaging ASAP to get to the benefits for themselves and their clients
- There’s plenty of innovation, from next-gen tech providers enabling new types of card programs to new forms of money that banks must address rapidly
- AI has been used in payment use cases for over a decade. Now, GenAI could provide a step change. However, fraud professionals must tread carefully
Product and capability innovation
- Winning/retaining deposits and loans will be even more crucial. Higher-for-longer interest rates, fintech offerings and a yearlong expansion of banking features by digital brokerages mean the continued fracturing of customer relationships
- Banks will increasingly offer targeted and differentiated product propositions (often via integration with segment-focused fintechs). Large and small institutions chase a broader market with new, all-digital brands to extend the reach and open deposit-gathering opportunities beyond their physical footprint
- This will drive product development investment and the creation of customer-centric bundles that allow for product, pricing, terms and feature customization to meet customer and regulatory demands. Banks must create enterprise services, spanning individual product systems to support sales and service functions
- Besides increasing speed and agility, cloud will determine how and what financial institutions migrate. In addition to intelligent automation, prime technology investment will include a growing interest in low-code tooling for business-critical applications
- GenAI will be embedded in DevOps, accelerating modernization, new development and testing
Emerging technology
- GenAI is now a consumer service. What started as a global stateless currency has evolved into routine use cases.
- GenAI, metaverse, AR/VR and quantum computing are being explored or evaluated by many banks and will have a significant impact on the market in 5 years’ time
- GenAI is moving from initial experiments to value delivery. Many vendors are incorporating GenAI into their offerings with cloud (and other) platforms, bringing foundation models and environments to develop and scale solutions. However, GenAI must be handled with care and guidelines
- The private sector is ahead of central banks in developing and launching digital money. With proven value in select use cases, initiatives must scale. Only a few central banks have launched CBDCs (to a lukewarm response). The ECB has just approved the next phase of its Digital Euro project, and European banks must engage to influence development
- In Europe, the momentum is shifting towards digital identity with large-scale pilots testing the European Digital Identity (EUDI) wallet. U.S. banks should monitor digital identity while continuing to improve traditional IDV approaches
Retail banking IT spending forecast
- IT spending in 2022 continued 2012’s recovery, with global spending rising to 4.3%. A similar increase (4.4%) is expected, reaching $261.3 billion in 2023. This is lower than projected (5.2%) mainly because of weaker growth in Tier 2 and Tier 3 U.S. banks
- The 2024 outlook is even more positive. Celent expects IT spending to reach $274.4 billion, an increase of 5.0% over 2023
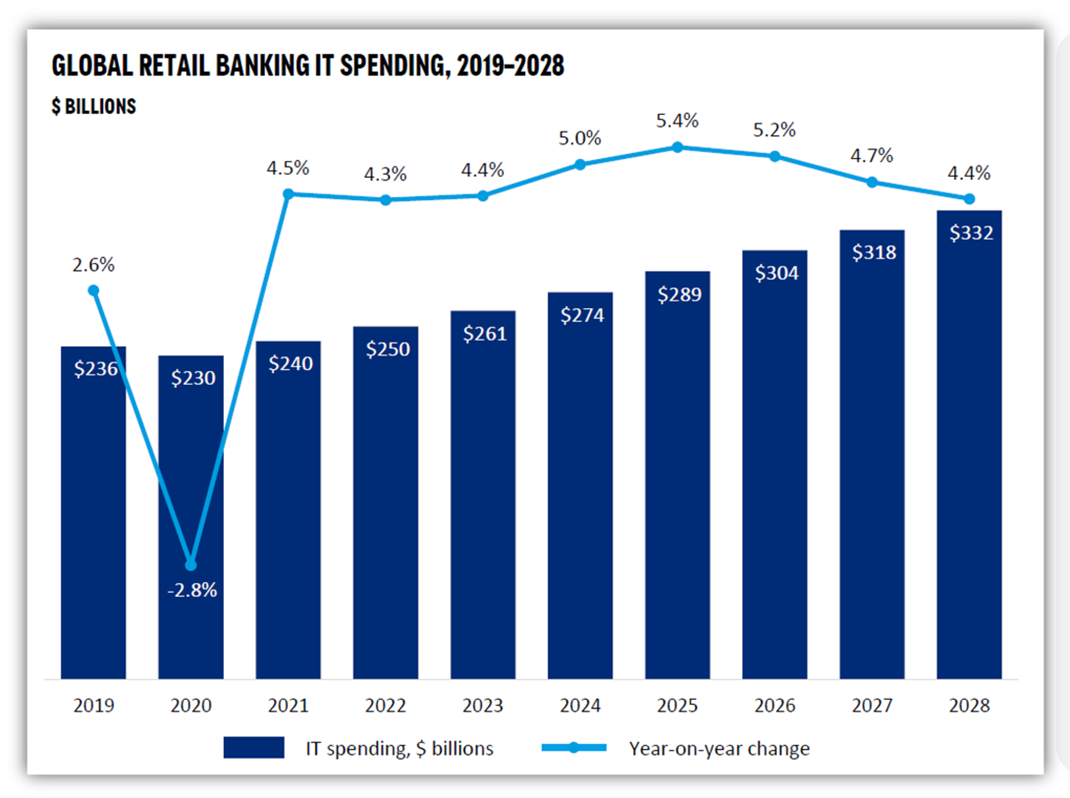
Source: Celent – Retail banking IT spending forecast 2023-2028
- Medium-term IT spending is set to grow as banks pull focus on digital transformation, driving investment in modernization, security, automation and digital engagement
- Celent expects stronger short-term growth, peaking at 5.5% in 2025. In 2024, a 5% increase is expected
- Growth will slow as banks try to extract cost benefits from application rationalization, modernization and cloud migration
- IT intensity (IT spending as a proportion of non-interest expenses) has risen steadily over the last decade, with many banks attempting to curtail growth or even reverse IT spending as a proportion of overall operating costs
Core banking systems: Mainframe or cloud?
According to IDC’s recent Future of Digital Infrastructure Worldwide Sentiment Survey, 47% of financial institutions intend to keep production workloads on premises over the next 2 years, either on private cloud deployments or on dedicated, traditional platforms.
Whether on mainframe or server farms, traditional technological resources will remain in operation and form part of the organization’s innovation strategy for the foreseeable future. However, this depends on the bank continuing to develop new platform functionality or find ways to modernize elements and create business opportunities.
Banks with older technologies not considered for immediate transformation should plan to maximize their value, forming strategies that include go-forward development.
What goes/stays?
Many banking workloads will move to the cloud, but other applications (or parts thereof) will remain on dedicated mainframe resources. Consequently, banks need to plan for innovation in the core regardless of the deployment technology. The primary considerations for determining which bank workloads to migrate to the cloud include security, cloud costs, data sensitivity and compliance.
Financial services deployment landscape 2025
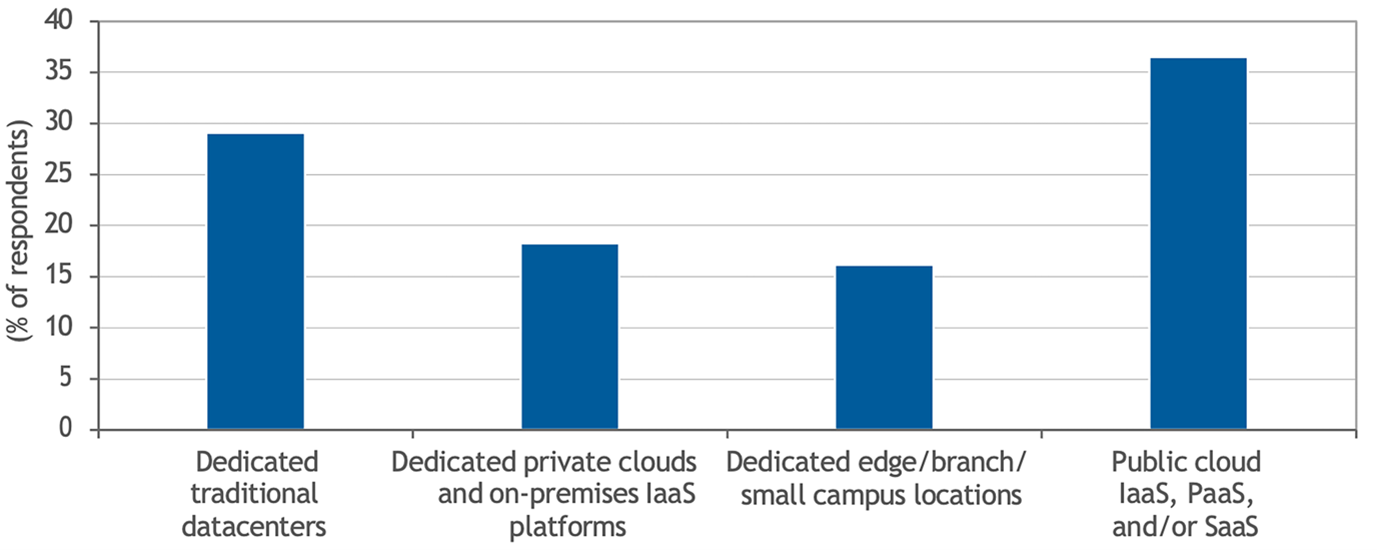
n = 133 financial institutions worldwide
Source: IDC’s Future of Digital Infrastructure Worldwide Sentiment Survey, June 2023
Cloud has become a transformative technology for the banking industry and continues to advance daily. Even so, the on-prem data center is still a critical deployment model for many financial services institutions as part of an overall fit-for-purpose infrastructure strategy.
Modern mainframes
Today’s mainframes still provide traditional high availability, highly secure and high-transactional throughput. But now they support microservices-based workloads, IoT, AI/ML workloads, modern development tools and agile development methodologies as well. These capabilities can be leveraged by core systems that are also modernized and remain on the mainframe.
Mainframe hybrid cloud strategy
Mainframe transformation supported by APIs, microservices and containers has given banks more freedom to decouple the business logic of the traditional, monolithic core and modernize/migrate pieces of the core system to appropriate platforms (including cloud), avoiding the considerable risk of wholesale platform migration. The institution might choose to keep some of the most critical core functionality (e.g., transaction processing, customer data and general ledger) on the mainframe by design.
Supportive partnerships
Virtually every global sector lacks the skilled staff to operate (let alone transform) their infrastructure. Consequently, to ensure that mainframe-based platforms continue to provide secure, resilient and scalable operations, using partners that understand banking business models and have the resources to work on existing systems and innovate will be critical.
Firms need to find partners that understand the banking rules about data sensitivity, regulatory compliance, resilience, performance and scalability. Prospective partners must also be experts in banking products and services to support ongoing development.
In addition to having the experience (and people) to understand the characteristics of mainframe development and operations, the right partner will have equal expertise in digital infrastructure, including cloud and edge, as these technologies must be perfectly meshed to maintain all the characteristics required by the banking industry.
Banking BPS market size and growth
Banking Business Process Services (BPS) refers to outsourcing specific business processes to third-party providers. Outsourced services aim to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs and enable banks to focus on core competencies.
The banking BPS market — valued at US$ 22.58 billion in 2022 — is projected to reach US$ 39.70 billion by 2030 (a CAGR of 11.11% from 2023-2030).
Primary factors driving market growth include increased lending and depositing, the increasing acceptance of digitalization, centralization and competition. The global banking BPS market report thoroughly analyzes key segments, trends, drivers, restraints, the competitive landscape and factors that play a substantial role in the market.
Market overview
Cost reduction is a significant driver for banking BPS. Outsourcing non-core processes enables banks to achieve cost savings through economies of scale, reduced operational expenses and optimized resource allocation.
Outsourcing allows banks to concentrate on core functions like strategic planning, customer relationship management and product innovation. They can enhance their competitive advantage by delegating routine and administrative tasks to BPS providers specializing in specific banking processes, efficient workflows and technologies. In this way, banks benefit from streamlined and optimized operations.
Banks can access advanced technologies, software and infrastructure through BPS providers, navigating complex regulatory environments effectively without substantial upfront investment. Providers often specialize in managing regulatory compliance and risk mitigation, too. Banks face the challenges of finding and retaining skilled personnel for specific functions.
Banking BPS market size and growth
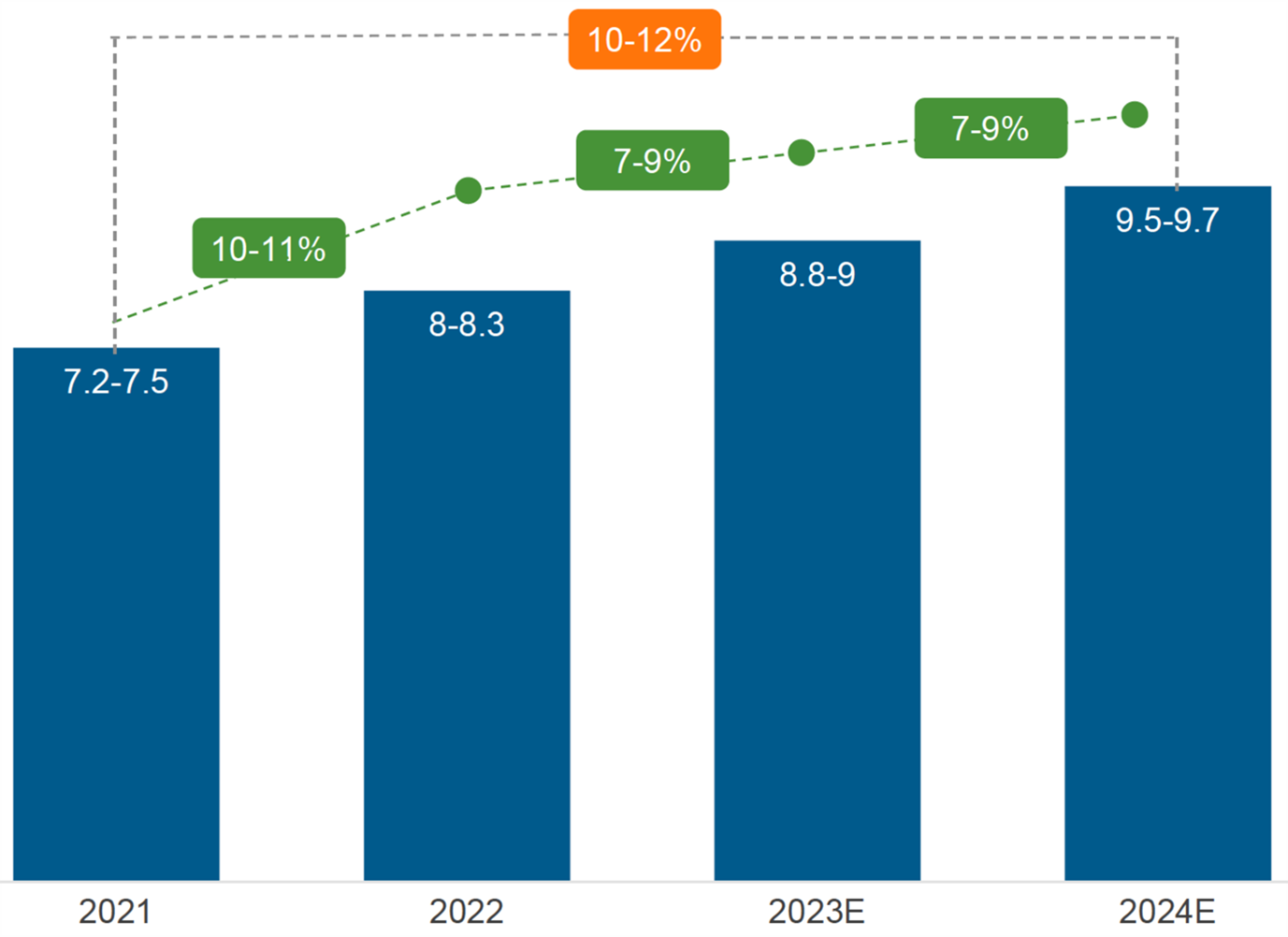
Revenue in US$ billion. Source: Everest Group – Banking Operations State of the Market 2023
- The global banking operations outsourced market grew by 10%-11% in 2022, with total spending crossing US$ 8 billion
- The 2021-2022 double-digit growth in BPS outsourcing came after 2020’s pandemic shutdowns. Cross-industry enterprises turned to outsourcing as a cost-cutting BCP lever and a strategic differentiator for providing frictionless, digital CXs. This was also fueled by increased demand for cards, payments and FCC operations
- Increasing adoption of digital banking services, cost-effective solutions and customer-centric services are driving market growth
- Key contributors are risk and compliance, mortgage and loan servicing, payment services and retail banking operations
Looking for more?
If you’d like to discuss further the opportunities that future AI-driven services and emerging technologies have in store, visit our website or contact us.
After all, “Someone’s sitting in the shade today because someone else planted a tree a long time ago.”