In brief
- Automated claims processing helps insurers increase productivity and profitability by resolving claims spikes, improving claims leakage assessment, enhancing customer satisfaction and net promoter scores, and establishing a 360-view of every claim and customer while optimizing data extraction, entry and verification
- Thanks to IoT data and AI-powered predictive analytics, customers can be notified when their insured property needs maintenance. The incentive for insurers to enable this preventative maintenance is simple. Helping customers avoid insured events is a lot cheaper than paying out after the fact
- Insurers rarely know precisely which bottlenecks and inefficiencies cause the most friction and compromise their profitability. Process mining helps insurers avoid focusing on solutions that have little impact by aggregating existing data and using AI to analyze and identify the most beneficial improvements. Process mining tools also help track KPIs across the company’s automation journey, highlighting what works best
Customer satisfaction has never been low on the insurers’ priority list. But today, it’s no longer defined exclusively by human interaction; digital experiences — or lack thereof — are just as crucial, if not more.
Claims processing can make or break a customer experience with an insurer. Accenture found that 74% of customers dissatisfied with how their claims were handled either changed or planned to change the provider. And the longer it takes the insurer to process a claim, the less happy customers are — understandably so.
Enter claims processing automation. Technologies like robotic process automation (RPA), optical character recognition (OCR), and artificial intelligence (AI) can accelerate claims processing by automating it partially or in full.
That, in turn, doesn’t only boost customer satisfaction and net promoter scores. It also optimizes costs, enhances employee productivity and powers data-driven decision-making.
At Zoreza Global, a DXC Technology Company, we help our clients attain these goals with intelligent automation solutions and our own LXA platform. Today, let’s tap into our experience and break down the underlying technologies, benefits, and challenges of automated claims processing, as well as how to implement it in the most efficient way possible.
Claims processing automation: What’s in the name?
Claims processing is a traditionally lengthy, paper-based process that requires hours of manual labor. In broad strokes, it consists of four main stages:
- The policyholder initiates a claim by notifying the company about an insured event
- The insurer processes the received documents to validate that the policyholder’s policy covers the stated event
- The insurer then assigns an adjuster to determine how the policyholder should be compensated and verify the claim isn’t fraudulent
- Once fraud is ruled out and the payment amount is determined, the policyholder receives the payment from the company
Automation can expedite each stage by removing the need for an employee or a customer to complete specific tasks manually.
For example, in the case of a car accident, the First Notice of Loss (FNOL) can be automated by IoT sensors transmitting the information about it without the customer’s involvement. Or, instead of initiating the claim by phone, customers can use a chatbot to file an FNOL.
Three key technologies powering automated claims processing
Claims processing automation isn’t one monolithic technology; it’s an umbrella term for using various technologies to replace human labor with software tools. Depending on the insurance claims processing workflow, one or several of these three technologies are worth considering.
Robotic process automation
Robotic process automation, or RPA, refers to creating programs, called bots, that complete a set list of rule-based actions to replace manual labor.
Instead of a developer determining what actions that list should contain, RPA tools analyze the user’s behavior in the graphic user interface (UI). Then, they repeat those interactions in the UI.
RPA is a low-code or no-code automation solution that can work with any system and application. However, it’s only suitable for automating simple, rule-based tasks, such as data entry or verification. RPA in health care claims processing, for example, can extract data from a claim filed online and add it to the core system.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
Artificial intelligence and its sibling technology, machine learning (ML), are versatile. They power several other technologies in automating insurance claims processing, such as the following five.
Optical character recognition (OCR)
OCR allows for transforming text in images into machine-readable data. This eliminates the need for manual data entry when the insured or third parties send scanned or photographed documents for claim processing purposes.
Computer vision
Consider it a more advanced version of OCR: Computer vision allows for identifying key features in images or videos. For instance, computer vision algorithms can analyze the dashcam footage to determine the scene and weather for car insurance claims processing.
Natural language processing (NLP)
This technology allows computers to understand the intent and meaning of spoken words and organic text. It can be used for claims processing by phone (which is still the preferred way to file a claim for 72% of consumers). NLP algorithms can identify specific claim data (location, date, etc.) and add it to a claims processing system, automating data entry as a result.
Chatbots and conversational agents
Chatbots can be simple rule-based bots that guide customers through filing claims and update them on their progress. However, AI-powered large language models (LLMs) enable chatbots to mimic human speech and provide a level of customer service that was previously impossible.
Advanced data analytics
AI and ML excel at finding patterns in swaths of data. In claims management, AI and ML algorithms detect potentially fraudulent claims or other suspicious behavior. They can also derive insights from claims processing data, such as speed, customer satisfaction, and cost, to identify areas for improvement.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things refers to the concept of using connected devices — sensors, wearables, smartphones and voice assistants — to collect data over the internet.
In claims processing, IoT data can give insurers accurate claim verification and adjustment data. It can also automate the FNOL; for example, the moment an airbag is activated during an accident, the insurer gets notified of a car accident.
How automated claims processing works stage-by-stage
All the technologies listed above can work in tandem to accelerate claims processing and make it less error prone. Here’s an example of how:
- Filing a claim. The FNOL can be fully automated in certain car and P&C insurance cases using IoT data. In other cases, the claim can be filed using a chatbot, an online form or an app. In case of filing a claim over the phone, NLP extracts claim data from speech
- Claim validation. All claim data is centralized in a claims management system using RPA. OCR transforms every scanned or photographed document into machine text. Computer vision processes images of the damage. RPA compares the described event with the customer’s policy and determines whether coverage applies
- Claim verification. Relevant third-party data (e.g., repair cost estimates) gets automatically collected and added to the system. RPA and AI algorithms assess the claim for potential fraud by comparing reported costs, damage, or event circumstances against data from other sources. In cases of potential fraud, a manual review is triggered
- Claim adjustment. AI algorithms suggest the appropriate payment amount according to the damage or costs incurred and the customer’s policy coverage
Three trends in claims automation to watch in 2024
The use cases and technologies we described above are already established go-to solutions for both insurtechs and forward-thinking incumbent insurers alike. However, there are also three emerging automation trends in automated claims processing worth paying attention to.
Preventative maintenance
Thanks to IoT data and AI-powered predictive analytics, customers can be notified when their insured property needs maintenance. This can apply to vehicles, industrial equipment and even home infrastructure like fire alarms.
The incentive for insurers to enable preventative maintenance is simple: It costs less to help customers avoid an insured event than to pay out when it happens.
Smart contracts
A smart contract is an “if… then” type of program that lives on a blockchain. Created by Ethereum in 2015, it represents a contract that automatically fulfills parties’ obligations when triggered by a specified event.
In insurance, blockchain and smart contracts gave a second breath to the concept of parametric insurance products. Instead of the insurance company assessing damage and making adjustments in every individual case, the simple fact that a certain event occurred (e.g., an earthquake) triggers a payment.
Smart contracts mirror the if-then logic, making them a perfect candidate for automating parametric insurance.
Drones
Drones are a cost-effective tool for more than just delivering shopping orders. In P&C insurance, they can help inspectors assess damage faster, more accurately, and more safely, all while reducing costs for insurance companies.
With drones, inspectors can easily view areas that would otherwise be dangerous, time-consuming or impossible to access (e.g., a collapsed roof after a hurricane). Drones can also record the damage for further assessment, including with automated computer vision tools.
Why automate claims processing?
In our experience, there are five common signs an insurance company stands to benefit from automated claims processing:
- A spike in claims, such as during a natural disaster, significantly slows down processing, leading to customer dissatisfaction
- An assessment of claims leakage — the difference between the actual and optimal payment caused by inefficiencies in processing — reaches as high as 20-30%
- Customer satisfaction and net promoter scores leave much to be desired, and customer churn correlates in time with claim settlement
- It is impossible to gain a 360-view of every claim and customer as data is disorganized and unstandardized
- Data extraction, entry, and verification remain a part of everyday workflows, resulting in a loss of productivity
Eight benefits of claims automation
Implementing claims processing automation allows insurance companies to reap the following eight benefits.
Decreased risk of human error
Manual data entry and verification increases the risk of human error, which can be costly for the company’s bottom line over the financial year. Automating just these two tasks can improve claims processing accuracy, enhancing the customer experience and saving costs.
Increased scalability and resilience
Automation tools can process thousands of claims without hiring more employees. What’s more, they can handle spikes in claims as efficiently as always, provided computing resources are easy to scale up and down. This makes both customer and employee experience consistently satisfying and optimizes costs at the same time.
Standardized, accurate, and comprehensive data
Automation is only possible by digitizing and standardizing data and aggregating it in a centralized data management system. This alone enables data-driven decision-making and allows for a 360-degree view of every claim and customer. It is also essential for other solutions, such as personalization at scale and Big Data.
Detailed audit trail
Introducing automation ensures that there’s always a digital audit trail for every case. Besides facilitating regulatory compliance and reporting, comprehensive and organized claims data is also a must for delivering swift and personalized customer service. It is also a prerequisite for seamlessly sharing data within an organization and with external business partners.
Mitigated risk of fraud
According to one estimate, fraud is a factor in 10% of P&C claims in the United States, resulting in annual $80 billion in losses for insurers. Claims processing automation is one way to make fraud detection more accurate: AI and RPA can weed out potentially fraudulent claims faster and more efficiently than any human employee could.
Reduced operational costs
More efficient fraud detection, reduced risk of human error, and more optimal human resource use all lead to one major benefit for insurers: Reduced operational costs. Emerging trends, like the use of drones for inspections, also contribute to improvements in the bottom line.
Better customer experience
The adjuster approach is the main driver of five-star reviews, followed by communication and process effectiveness. Automation allows adjusters to focus on going the extra mile for policyholders instead of tedious tasks like data entry. Plus, it enables tracking claim status, which enhances communication with the customer.
More satisfied and more productive employees
As employees no longer need to spend their working time on repetitive tasks like copying and pasting data from a filed claim to the internal system, they can dedicate their time to non-automatable tasks. Besides saving them hours of tedious work, automation also gives them a more profound sense of purpose, increasing satisfaction levels.
4 challenges of insurance claims automation
Of course, automating insurance claims processing isn’t without its pitfalls. Let’s break down the four most common ones.
Fragmented data
Data silos spread across fragmented systems, along with security concerns, hinder 70% of automation initiatives. That’s because automation is impossible without standardizing both processes and the underlying data.
How to overcome this challenge? If every department or branch stores data “their way”, the prerequisite to claims processing automation is implementing a unified data strategy and parking all data in a single data warehouse.
Old legacy systems
Insurers rely on outstandingly aged legacy systems: On average, they’re 18 years old, according to McKinsey’s data. While RPA is compatible with an application of any age (since it interacts only with the graphic UI), integrating other automation solutions can be challenging due to compatibility issues.
How to overcome this challenge? If the current automation needs can be met with RPA, there’s no need to modernize legacy systems. However, in other cases, insurers may need to replace, rewrite, rearchitect, or re-engineer their legacy IT estate before integrating advanced automation solutions.
Uncomprehensive approach
The overwhelming 92% of life and non-life insurers miss out on some of the value of process automation. Instead of automating whole workflows end-to-end (which may require reinventing them in the process), they focus on automating specific tasks within those workflows.
How to overcome this challenge? Before kicking off an automation project, insurers need to assess which processes could be automated in their entirety. Moreover, they should consider which processes can be reimagined to boost customer satisfaction (e.g., a fully automated FNOL using IoT sensors).
Potential legal issues
The use of insurance claims automation technologies can draw some heat in the form of class action lawsuits. Cigna was the latest to experience it: The health insurer was sued for allegedly automatically denying claims without human involvement in assessing health care services’ necessity. Plaintiffs argue that it violated California law.
How to overcome this challenge? First, insurers should investigate to which extent they can automate claims processing under their jurisdictions’ regulations. Second, to avoid lawsuits like the one Cigna is facing, insurers must maintain human governance in claims processing.
How to automate claims processing in 10 steps
To avoid common pitfalls — going over the budget, missing deadlines, or focusing on solutions misaligned with business goals — we advise our insurance clients to follow these ten steps in their automation journey.
Pinpoint strategic goals
Most organizations struggle with identifying opportunities for automation. To breeze through this challenge, it’s best to pinpoint the strategic goals behind the automation efforts. What should it achieve, in the long run, for the company?
The most successful automation programs, unsurprisingly, are the ones seeking to augment employee and customer satisfaction along with reducing costs and improving operational efficiency.
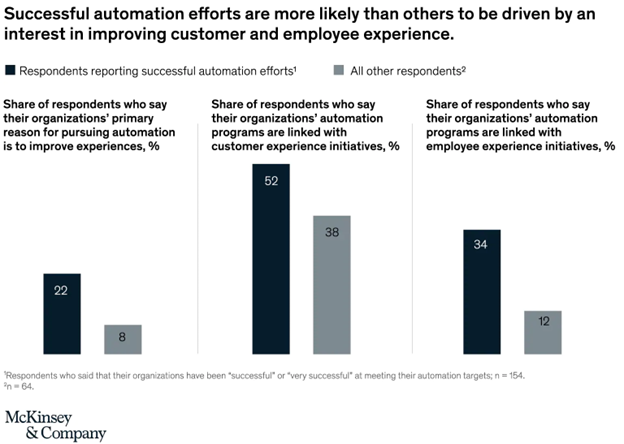
Image source: McKinsey and Company "Your questions about automation answered"
Determine the processes and workflows to be automated
Instead of trying to overhaul every process from the FNOL to claim settlement in one go, prioritize the processes that need to be automated first. This approach will help maintain buy-in and demonstrate value quickly. To assess processes, consider:
- Business impact
- Process maturity
- Process complexity
It’s also crucial to rely on customer and employee feedback to determine which processes create the most friction for them. We advise mapping the customer journey to put policyholders’ experiences front and center in automation efforts.
Once priorities are set, determine the specific workflows that need to be automated. At this stage, it’s important to remember — some workflows may have to be reimagined before automation can be introduced.
Use process mining
Insurers often don’t have a clear, comprehensive picture of which bottlenecks and inefficiencies cause the most friction and affect the bottom line. To avoid focusing on solutions that have little impact on the strategic goals, consider turning to a process mining strategy.
Process mining refers to aggregating data from existing systems and analyzing it with AI to identify key opportunities for improvement. A process mining tool will also help keep track of KPIs throughout the company’s automation journey, giving decision-makers an idea of what works and what doesn’t.
Assess risks
Implementing claims processing automation, like any other automation effort, comes with certain risks that need to be identified and addressed. Those risks include:
- Security and privacy
- Fairness and transparency
- Safety and performance
- Third-party risks
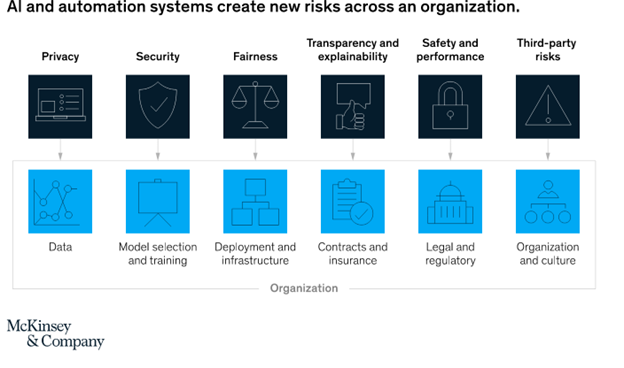
Image source: McKinsey and Company "Managing the risks and returns of intelligent automation"
The specific risks depend on the solution chosen for claims processing automation. To enable risk-driven decision-making, you need to compile a list of potential solutions and assess their vulnerabilities and risks one by one.
A dedicated team should continuously monitor those risks across the organization after the solution’s rollout.
Involve non-technical employees
Automation leaders don’t only focus on employee and customer satisfaction; they also involve their employees in the automation efforts. In fact, 44% use the human-in-the-loop design method, where non-technical employees help train automation technologies.
This approach bears fruit as employees are the ones with hands-on knowledge of routine workflows and tedious tasks that can be automated. So, get them involved in the project early on and make them a part of the team.
Determine functional and technical requirements
Will a SaaS solution meet the company’s automated claims processing needs? Or is bespoke development in order? Which technologies are best equipped for automating the selected workflows? Is AI a must, or will RPA do the trick? What applications should the automation solution integrate with?
Consider all these questions to zero in on your automation needs. Then, translate those needs into requirements falling into one of these two categories:
- Functional requirements. These are the features users should have access to as a result of automation. For example, customers seeing and validating prefilled fields in the FNOL form is a functional requirement
- Technical requirements. These describe how the automation solution should be built, what technologies should be used, and what integrations should be available. For instance, it may have to be compatible with a 20-year-old legacy system or support REST API calls
Remember about human oversight
While automating insurance claims processing from A to Z may seem alluring, it’s vital to keep in mind that algorithms are created by humans. And humans make mistakes or overlook certain scenarios (besides, automatically declining claims may pave the way for class action lawsuits).
That’s why human oversight is still required in claims processing, and it has to be embedded into the solution from the get-go. So, think through the automation governance before settling on a solution.
Break silos
An insurance company may have dozens of disparate applications for every department, from CRMs to sales and regulatory compliance systems. But, as mentioned above, fragmented systems and siloed data are one of the key challenges of introducing automated claims processing.
That’s why insurance companies should first review their data management strategy before introducing automation. Only once there is a single source of truth for data across the organization, automation can bear fruit.
Start with a pilot project
Any automation effort should start with a proof-of-concept. It allows for promptly demonstrating value and improving or maintaining buy-in, for example. It also helps determine whether key assumptions about the automated processes are valid.
Based on the pilot project’s results, decision-makers can choose to:
- Proceed with automation on a larger scale
- Improve or change the solution and do another iteration of the pilot project to test it
Roll out and track progress
While most automation leaders opt for large changes to processes instead of incremental improvements, that doesn’t mean that the rolled-out solution should be carved in stone. The iterative approach to polishing off the solution is still an effective way to ensure automation sets the company on a trajectory to meet the set goals.
To that end, insurers should keep track of the KPIs and user feedback after the rollout. Based on the collected information and the type of solution, decision-makers may need to rethink or redevelop certain automation processes or account for previously overlooked scenarios.
How Zoreza Global powers claims processing automation with LXA
At Zoreza Global, we excel at intelligent automation solutions and are the force behind the LXA platform, a claims automation engine.
LXA uses advanced data analytics to inform automation efforts. Integrated with Tableau, Snowflake and Dataiku, LXA is a single solution for claims that brings together:
- Claims database
- Supplier databases
- External data
- Policy database
Powered with data analytics, LXA enables:
- Automatic validation and routing for injury and legal cost assessment and the FNOL
- Fraud scoring and anomaly identification
- Data prepopulating using multiple sources
- Estimate creation of the FNOL and injury and legal cost assessment
If you’d like to learn more about LXA, we invite you to check out our detailed breakdown of how LXA can transform claims processing.
Ready to make your claims processing lightning-fast?
Automation can make customers and employees happier, reduce costs, and improve scalability and accuracy — but only when implemented correctly.
Let us lend you our expertise to ensure your project attains its goals. Reach out to us to discuss how intelligent automation solutions, including our LXA platform, can supercharge your claims processing.
Don’t know if your organization is ready for digital claims? Take our self-evaluation quiz to get a claims processing assessment in just five minutes!