In brief
- ESG data refers to KPIs that are used to assess the organization’s environmental and social impact and governance. It can also be used to evaluate the organization’s progress in meeting sustainability goals, whether they’re set internally or imposed by regulators
- As banking systems are, on average, 14 years old among universal banks, unaddressed technical debt can hinder even the most well-thought-out data-collection efforts. Without addressing legacy systems first, achieving a seamless flow of data into the ESG data management solution can be almost impossible. Breaking those data silos first is imperative
- Your ESG strategy may already include specific goals like the share of investment dedicated to renewable energy projects or the amount of carbon emissions. But if it doesn’t, you may need to set explicit, measurable goals with specific metrics to be tracked to monitor your progress
While banking wasn’t initially in the crosshairs of the push for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) accountability, that’s no longer the case.
For one, consumers expect their financial institutions to demonstrate their sustainability performance with ESG data — and offer sustainable financial products. In the United States, almost two out of five eligible consumers are interested in signing up for at least one green financial product. At the same time, only an estimated 10% of all demand for sustainable global transaction banking is met.
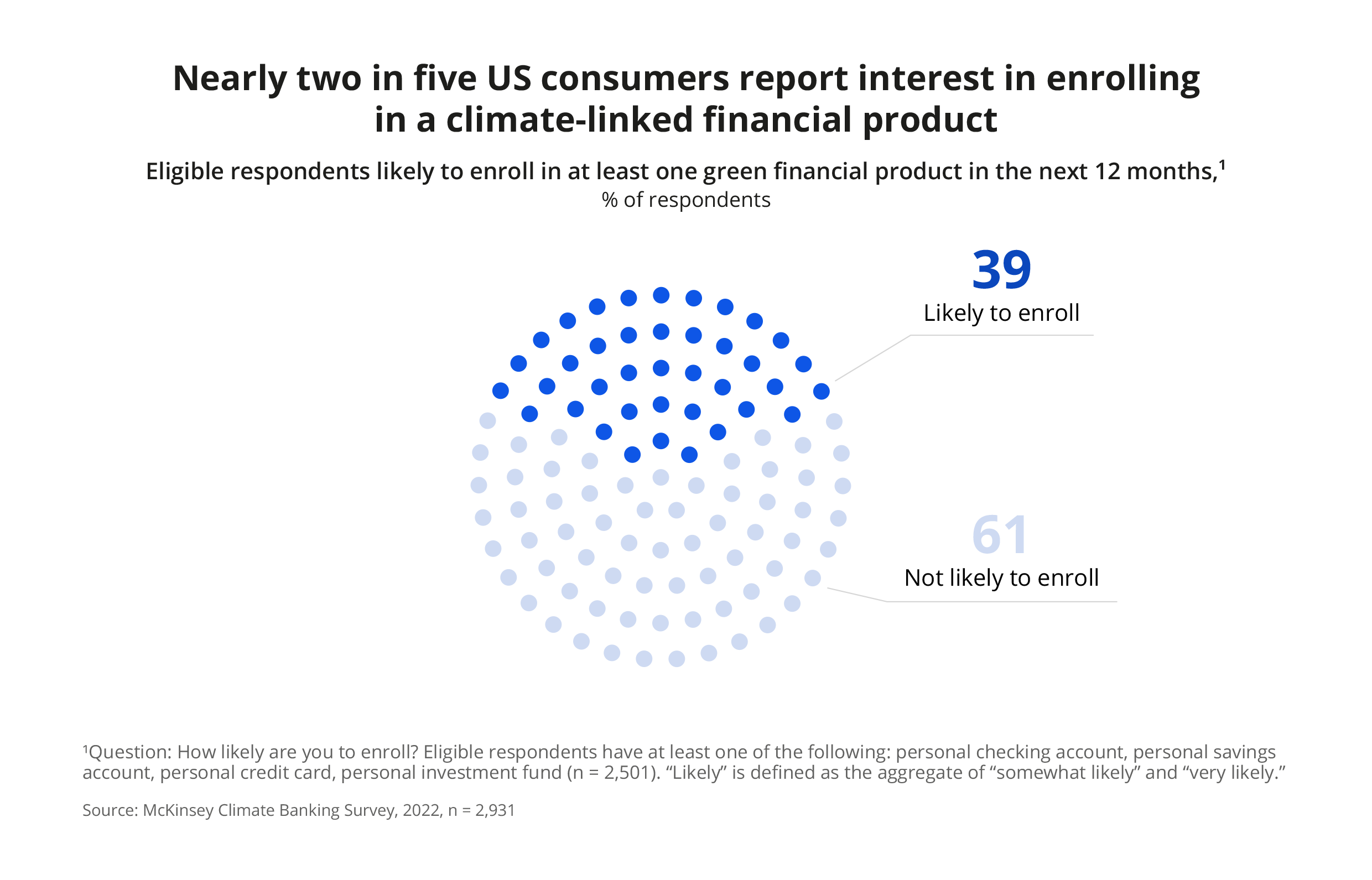
But consumers aren’t the only ones driving the need for sustainability in banking. Investors increasingly rely on ESG data to drive their decision-making. According to one 2023 survey, 79% of investors consider how the company manages sustainability risks and opportunities when making decisions.
Regulators in certain jurisdictions also make ESG reporting mandatory. For example, in the European Union, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive entered into force on January 5, 2023, and now mandates all large companies and listed enterprises to report ESG data.
However, ESG reporting is easier said than done. The lack of universal ESG metrics accepted across jurisdictions and frameworks quickly turns it into an ordeal. The lack of a sound ESG data management strategy can also undermine any progress in that regard.
Here’s what you need to know about managing ESG data, from how to collect it to what challenges you should keep in mind.
What is ESG data?
ESG data refers to key performance metrics (KPIs) that are used to assess the organization’s environmental and social impact and governance. It can also be used to evaluate the organization’s progress in meeting sustainability goals, whether they’re set internally or imposed by regulators.
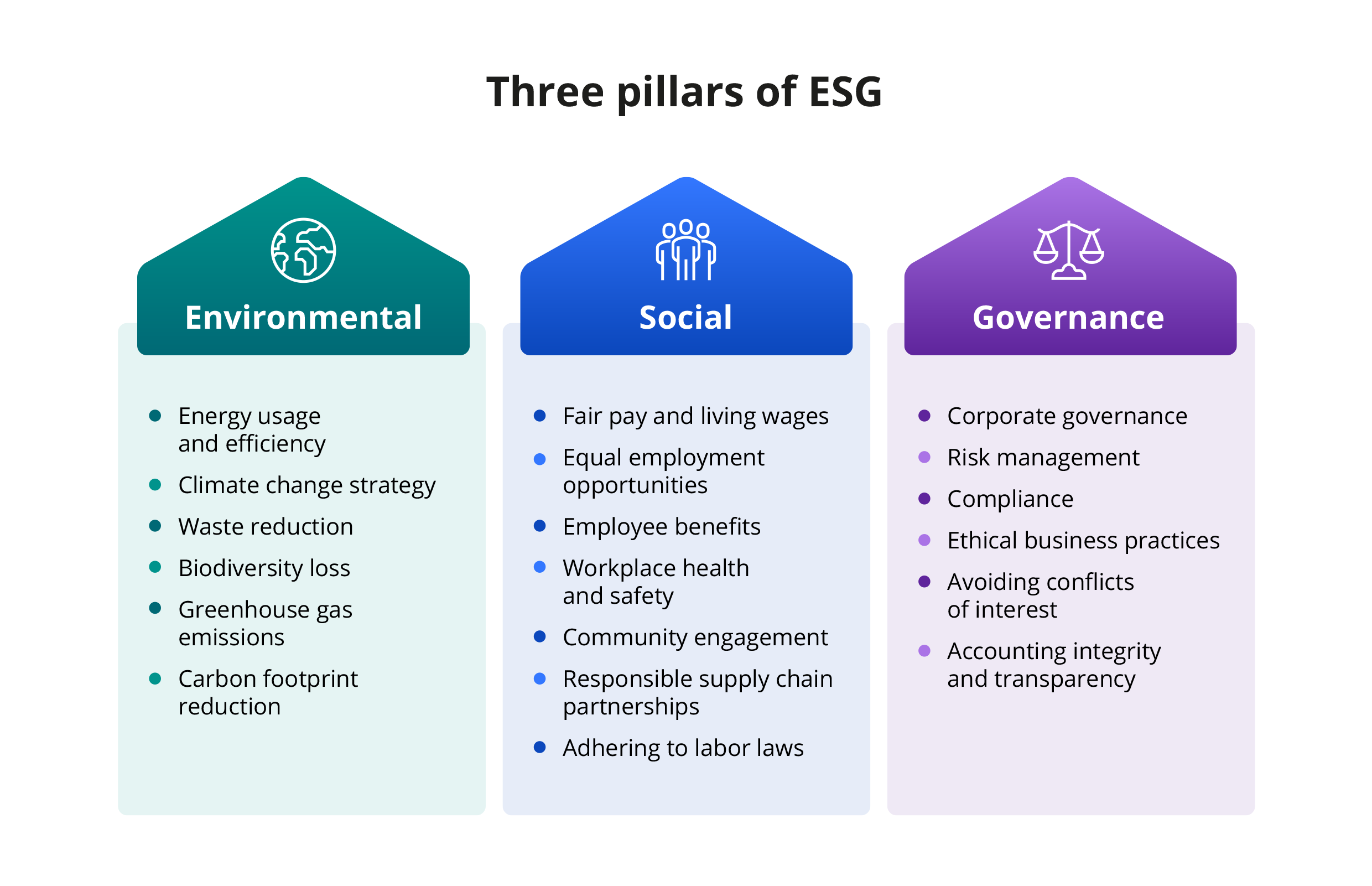
ESG itself stands for:
- Environmental impact. This data reflects the organization’s adherence to sustainability practices through the lens of greenhouse gas emissions, waste management, deforestation, biodiversity, and more
- Social impact. This group of metrics assesses the organization’s impact on people and communities, its diversity and inclusivity progress, supply chain management, and respect for human rights
- Governance. This data examines the organization’s governance practices, such as executive compensation, shareholder rights, and board management practices
4 benefits of comprehensive ESG data collection
When done right, ESG data collection and reporting is more than meeting reporting requirements imposed by sustainability regulations. It can be a powerful asset in informing your ESG strategy, minimizing risks, and attracting investors.
Data-driven ESG strategy
Objective, reliable data is key to maximizing the efficiency of any sustainability efforts and ESG strategies. This data can inform the organization’s ESG strategy, demonstrating which sustainability initiatives succeed and which ones fail. It’s also crucial for understanding whether the organization reaches its goals at all.
Performance monitoring
ESG data can provide insights into why the company's ESG initiatives succeed or fail — and where allocating resources will have the highest impact possible. This will help you ensure your organization stays on track to achieving its ESG goals while ensuring efficient resource allocation.
ESG investing opportunities
Investors are paying more and more attention to the ESG data when making decisions, too. According to the 2023 PwC Global Investor Survey, 85% of investors would like to see ESG disclosures treated the same way as financial statement audits. Therefore, comprehensive ESG reporting becomes a factor in attracting investors.
Enhanced risk management
Collecting data on ESG not only helps meet stakeholder expectations. It also gives you a better overview of risks associated with climate change, transition to renewable energy sources, etc. ESG data can then enable better risk management and deliver insights into new opportunities that arise together with risks.
4 ESG data management challenges in banking
Of course, ESG data management isn’t without its challenges. In our experience, the following four are the most pressing ones you should look out for.
Disparate ESG standards
Collecting and publishing ESG data has remained largely voluntary up until now. Therefore, what data is collected and analyzed still tends to vary widely.
Today’s common frameworks for reporting ESG data all use varying metrics. Those are:
- International Sustainability Standards Board (IFRS) Standards. The IFRS Foundation was tasked with the responsibilities of the Task Force of Climate-Related Disclosures after it was disbanded in 2023
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards. This framework is used by over 14,000 organizations across 100 countries and includes universal, sector-specific, and topic-specific standards
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) Standards. This framework spans 77 industry-specific standard sets, including the standards for the finance industry
Technical debt
As banking systems are on average 14 years old among universal banks, unaddressed technical debt can hinder even the most well-thought-out data collection efforts.
Without addressing legacy systems first, it can be nearly impossible to ensure the seamless flow of data into the ESG data management solution. Breaking those data silos first is imperative.
Lack of quality data
While legacy systems are typically at the source of data silos, ensuring the flow of data isn’t the only challenge. The data supplied to the ESG data management solution should also be accurate and reliable; otherwise, it’s “garbage in, garbage out.”
Operational silos
Collecting and reporting ESG data is an organization-wide undertaking as ESG data concerns everything from supply chains to energy consumption and sources. While centralized governance over ESG data management is necessary to standardize the data, it has to be a joint endeavor of business and IT functions — and involve all internal stakeholders.
Collecting ESG data: 4 considerations to start with
Before you can implement an ESG data management platform organization-wide, you need to consider the following four aspects of your data management strategy.
Data types
Before you start collecting ESG-related information, you need to ensure you track the right metrics. To identify relevant data, you can use one of the frameworks listed above (IFRS, GRI, SASB). However, take into account regulatory reporting requirements to ensure the ESG data you collect meets them.
Data sources
Where will the ESG data be coming from? Identify the data sources and determine who will be in charge of supplying specific types of data. For example, certain governance data can come from financial reporting tools already in use.
You can also collect data from third-party data providers. For example, certain environmental data, like energy consumption, can be automatically collected from energy providers.
Pay attention to ESG data gaps. These gaps are the metrics that you lack data on at the moment. You’ll need to close these gaps before adopting an ESG data management platform.
Data quality
To avoid misleading data, you need to ensure data quality at the source. Data quality means:
- Completeness: The data doesn’t have missing values
- Data accuracy: It accurately reflects the measured metric
- Consistency: All metrics follow a unified standard
- Uniqueness: There are no duplicate entries or values
- Validity: The data matches the required format
- Timeliness: Data is provided when needed
Data security
The ESG data may include some sensitive information, such as financial performance metrics or employee data. Pay attention to protecting that data from unauthorized access with a combination of identity verification processes and encryption.
Your roadmap to succeeding in ESG data management
Ready to embark on the ESG data management journey? Here are the six steps toward successful ESG data collection and reporting.
Know your data
Before you collect ESG data, take stock of the ESG data you already have, where it is, in what format it comes, and which data you lack. Identify the right metrics and data sources; determine how you’ll ensure data quality and how you’ll resolve data gaps.
Involve both internal and external stakeholders in these processes to ensure:
- The collected data meets investors’ expectations and regulatory requirements
- You have a full overview of the available ESG data and data gaps
Set up data governance and controls
Who will be in charge of collecting the ESG data and ESG reporting? Before you implement a data management solution, ensure you have a single point of contact for ESG data management.
This typically means appointing an ESG data officer and creating an ESG data governance committee. That said, your whole organization has to be aligned with your ESG data management strategy, across departments and management levels.
Beyond governance, you will need well-thought-out data controls — the policies and procedures that dictate how you will collect, manage, process, and report on the acquired ESG data. Needless to say, ESG data controls have to be aligned with existing internal protocols and regulatory requirements.
Set your goals
Your ESG strategy may already include specific goals like the share of investment dedicated to renewable energy projects or the amount of carbon emissions. But if it doesn’t, you may need to set explicit, measurable goals with specific metrics to be tracked to monitor your progress.
Adopt an ESG data management solution
The system that will collect ESG data has to be your single source of truth for the said data. Here are the markings of a good ESG data platform:
- Integrations with relevant data sources (e.g., core banking system, financial reporting tools)
- Automated data aggregation, validation, and verification
- Data analytics to derive insights from the data
- Comprehensive report generation functionality
- Real-time ESG data visibility for investors
- Regulatory compliance with applicable regulations in ESG reporting, privacy, and data management
- Powerful automation capabilities for analytics, reporting, etc.
- Sufficient flexibility for adapting to changing requirements
If you’d like to leverage ESG data management expertise at this stage, a partner like Zoreza Global can help you conduct a buy vs. build analysis and select the right vendor if you opt for an off-the-shelf solution.
Update workflows
ESG data collection and assessment have to be included in all relevant processes across your financial institution. Update all relevant workflows to enable ESG data reporting and communicate ESG requirements to internal stakeholders, from C-level management to employees.
Stay on top of evolving ESG requirements
If your organization is subject to mandatory ESG requirements, ensure your ESG data management team is on top of the latest changes in those requirements. Your compliance team has to work closely with their ESG colleagues to that end.
As for the voluntary ESG reporting, make sure you — and your ESG data platform — stay up-to-date with changes in the selected framework’s metrics.
Are you ready for ESG data disclosure?
To answer this question, compare your current ESG data management against these six best practices:
- Automation. ESG data collection, validation, verification, and aggregation are largely automated, with data analytics helping derive insights from it
- Standardization. ESG data management is consistent across the organization to ensure the data is reliable, accurate, and fit for purpose
- Clear data governance. There is a centralized oversight over ESG data collection, analysis, and reporting
- Data validation and verification. All collected data is checked against the pre-defined data quality criteria to ensure its accuracy and reliability
- Single source of truth. Your organization has a single source of truth for all ESG data to prevent inconsistent or disparate data
- References. All ESG data can be traced to its origin to facilitate internal audits and reporting for external stakeholders
ESG data collection is a strategic investment
While meeting regulatory or industry requirements remains the number one reason for addressing ESG topics in financial services, it’s far from the only one. While 46% of financial services organizations strive for compliance, 32% leverage ESG policies to promote growth. An equal share of respondents, 32%, address ESG topics to meet investor requirements.
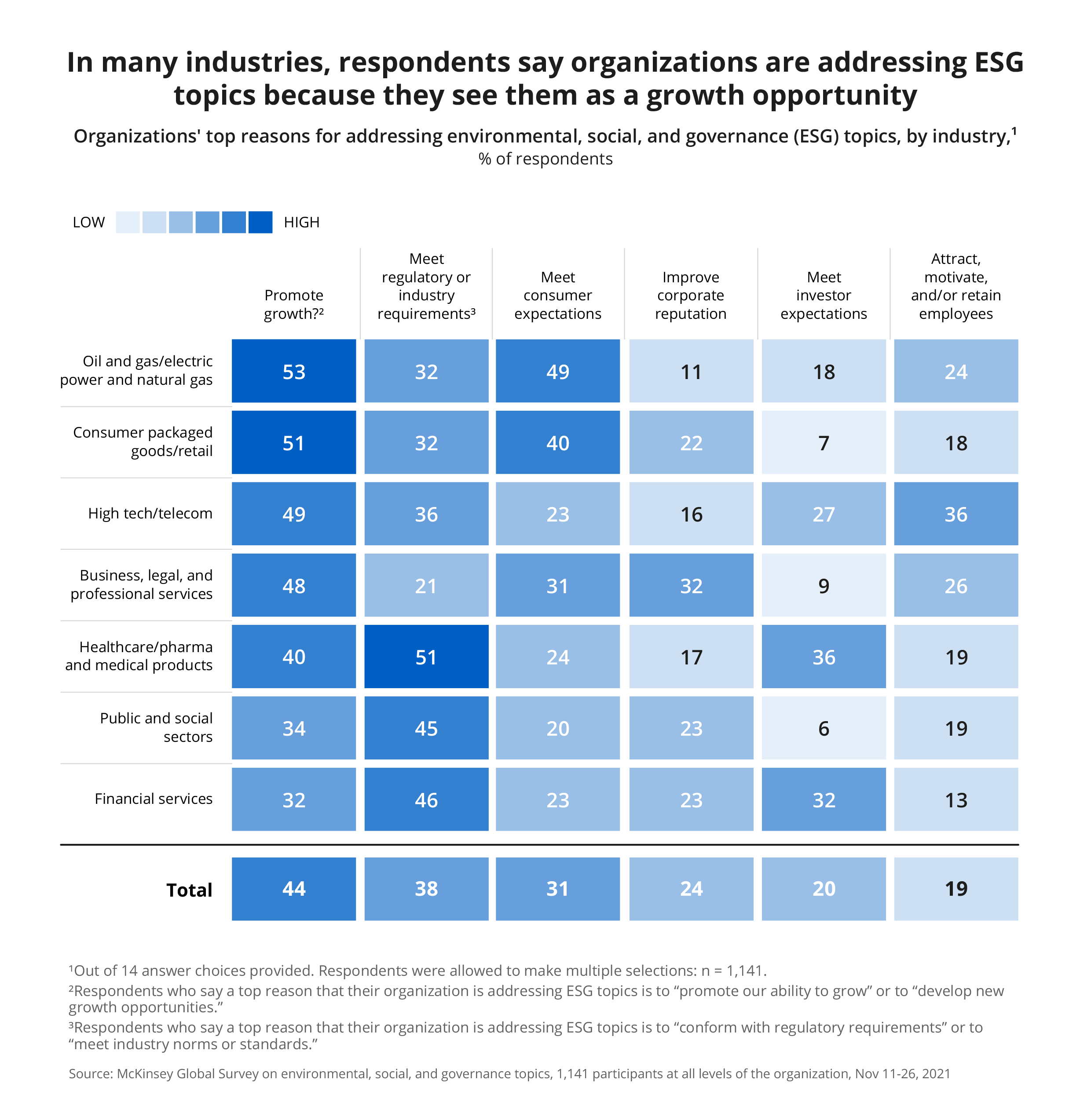
With the mounting regulatory pressure to ensure sustainability across industries, especially in the European Union, tracking ESG data is already a must for many financial institutions. However, the increasing interest in ESG investing also makes the case for implementing data-driven ESG policies as a long-term investment.
Zoreza Global can help you make the most out of your ESG data
With 45+ years of experience in technology solutions for banking, we have what it takes to help you design and implement a comprehensive ESG data management strategy that will become your competitive advantage.
To that end, we combine our industry acumen with expertise in data analytics, automation, and cloud, as well as vendor solutions and bespoke engineering. As a result, we’re well-versed in common challenges banks encounter during their data transformation — and we remain well-equipped to address unique problems that may undermine your efforts.
For example, we have already helped a Swiss cantonal bank integrate ESG data management with the wealth management solution for its investment business.
Reach out to us to discuss how our expertise in ESG data management can help you make the buy vs. build decision, select the right vendor solution and seamlessly integrate it into your software stack, or get a bespoke solution to meet your needs.
Setting up the ESG data management strategy is only the beginning
To make the most out of your ESG data, you need to do more than just report it to comply with requirements. The ESG data can be a powerful asset in guiding your organization toward attaining specific ESG goals, enhancing your risk management, improving resource efficiency, and meeting investor expectations.
However, to do all that, you need to ace the first step in the journey — implementing a sound, effective ESG data collection and management strategy. Get in touch with our ESG data management experts to discuss how Zoreza Global can help you do exactly that.
References
- What is data quality? IBM, May 2023
- ESG reporting: challenges and opportunities for financial institutions, BankingHub, March 28, 2022
- Green growth: Unlocking sustainability opportunities for retail banks, McKinsey, April 21, 2023
- ESG momentum: Seven reported traits that set organizations apart, McKinsey, May 26, 2023
- How to keep your ESG data from managing you, Thomson Reuters, January 23, 2023
- Sustainability in global transaction banking: A market imperative, McKinsey, October 7, 2022
- What is environmental, social and governance (ESG)? IBM, January 24, 2024
Want to know more?
To discover more about why reliable data is key to maximizing the efficiency of sustainability activities and ESG strategies, visit www.luxoft.com/industries/capital-markets/regtech-solutions. However, if you have a particular data management issue you’d like to discuss, contact us.








