In brief
- Industry 4.0 or the fourth industrial revolution, leverages technologies like IoT, AI, and cloud computing to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making
- Successfully navigating these challenges can bring substantial benefits such as improved efficiency, enhanced decision-making capabilities, increased customer satisfaction and a competitive edge in the market
- Adopting a comprehensive digital culture that embraces continuous learning and robust cybersecurity measures is crucial for businesses to fully exploit the potential of Industry 4.0
In the current software-defined business environment, the challenge of digital innovation marks the divide between organizations that have harnessed the full potential of new-age technologies and those that lag behind. This divide, also known as the "digital innovation gap," separates competitive organizations from those that continuously try to keep up with Industry 4.0, the fourth industrial revolution.
Industry 4.0 represents a new era in manufacturing, driven by the rise of IoT, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, big data analytics, digital twins, cyber-physical systems and other emerging technologies. Bridging the "digital innovation gap" results in enhanced production efficiency, higher ROI, streamlined operations and improved quality control.
The journey toward Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 extends beyond merely comprehending new technologies; it entails recognizing the transformative potential they possess and streamlining processes to meet increasing business demands. Bridging the digital innovation gap requires a multifaceted strategic approach, which will ensure both businesses and employees are equipped with the tools and knowledge needed for successful digital transformations. Grasping the concept of Industry 4.0 is the initial step toward a comprehensive understanding of the evolution in manufacturing, its present state and the potential for future growth.
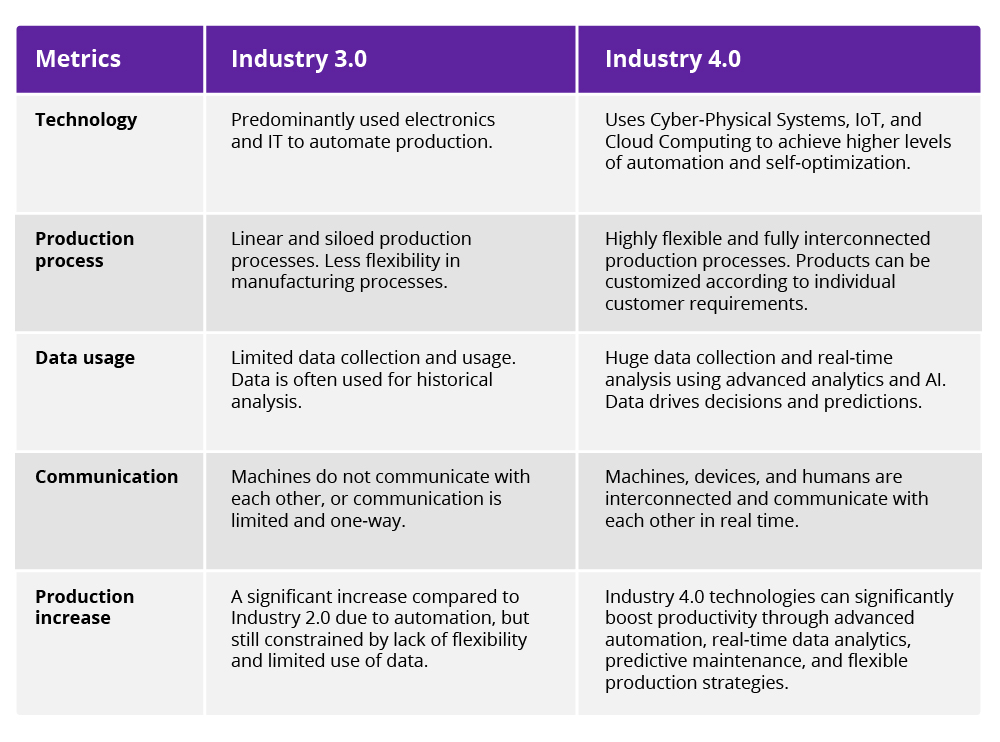
Industry 4.0: An evolution, not a revolution
Industry 4.0 is a logical progression rather than a radical shift from previous industrial revolutions. It involves the seamless integration of cutting-edge technologies to streamline operations, improve data management and automate manufacturing facilities. AI, cloud computing, advanced analytics, complex ML systems, additive manufacturing and other emerging technologies define the new era in human-machine interaction and represent the next phase in advanced engineering.
Real-time data integration improves operational efficiency and enables immediate decision-making. IoT devices serve to monitor and streamline supply chain management, while AI and ML shorten downtime by preventing equipment failures before they occur and minimizing human intervention in quality control. These transformations result in superior product quality, delivered more efficiently and cost-effectively, thereby improving the customer experience.
Apart from the transformative impact Industry 4.0 brings to manufacturers, it significantly affects the broader business ecosystem. Its potential is far-reaching and holds the key to reshaping the future of manufacturing.
Navigating the challenges of Industry 4.0
While Industry 4.0 holds the promise of a more efficient and productive future, this transformation comes with a set of challenges businesses should be prepared to encounter:
- Data privacy and security. The proliferation of interconnected devices increases the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks. Protecting data privacy and ensuring security, which are of high importance among large manufacturers, become critical challenges for successful implementation. Additionally, interoperability between different IoT systems can become a barrier to smooth integration, which will increase the time required for preparation and demand additional investment. Ensuring real-time data collection and analysis requires significant computing power and bandwidth
- High entry cost. Transitioning to Industry 4.0 requires substantial capital investment in new hardware, software, infrastructure and human resources. This cost includes upskilling and reskilling employees to use and maintain these systems. Upskilling is the process of educating existing employees and helping them acquire new skills required to work with new equipment or software. Reskilling is more challenging, especially for SMEs, as employees need to be trained to acquire new skills to change their roles in an organization. Such education programs are usually costly and time-consuming
- Technological compatibility. Existing legacy systems used by manufacturers are often outdated, which makes migration to new platforms and systems challenging. Retrofitting or replacing old systems can take time, require significant investment and involve building new partnerships with software development vendors
- Skills gap. Meeting the demands of Industry 4.0 requires a skilled and professional workforce knowledgeable in new-age technologies. However, with the current shortage of employees having the necessary digital experience, hiring new employees might become a challenge even for a well-developed enterprise
- Regulatory restrictions. For international organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions, complying with regulations, labor laws and industry-specific requirements might become the key barrier to bridging the digital innovation gap
Despite all the challenges, Industry 4.0 can pave the way for substantial business growth. Companies investing in advanced cybersecurity measures and comprehensive employee training programs benefit from an improved supply chain and more efficient production. Collaboration through partnerships or consortia can help businesses attract new investment and share the cost of digital transformation, making it manageable for even small and medium-sized enterprises.
Successfully addressing these challenges will pave the way for organizations to fully leverage the transformative potential of Industry 4.0 and reap its long-term benefits.
Unleashing the potential benefits of Industry 4.0
Upon bridging the digital innovation gap, manufacturers can reap a set of advantages that have the potential to transform the industrial landscape and the global economy as a whole:
Efficiency enhancement. Real-time data processing and increased automation result in streamlined operations and reduced waste, fostering an environment of improved operational efficiency.
Flexibility improvement. Increased automation enables companies to swiftly respond to changes in demand or production, allowing for a broader range of customized products and services.
Improved decision-making capabilities. AI and ML platforms and systems enable the processing and analysis of large volumes of data, facilitating predictive decision-making at both strategic and operational levels.
Customer satisfaction amelioration. Quality control improvements, shortened production times and personalized products lead to an enhanced customer experience and improved satisfaction rates.
Competitive edge. Manufacturers who embrace the fourth industrial revolution are likely to gain a competitive advantage through improved efficiency, flexibility and optimized decision-making.
All these benefits create a chain reaction. Increased efficiency leads to cost savings, which can be reinvested in other areas such as research and development. Enhanced decision-making capabilities result in production enhancement.
Key technologies powering Industry 4.0
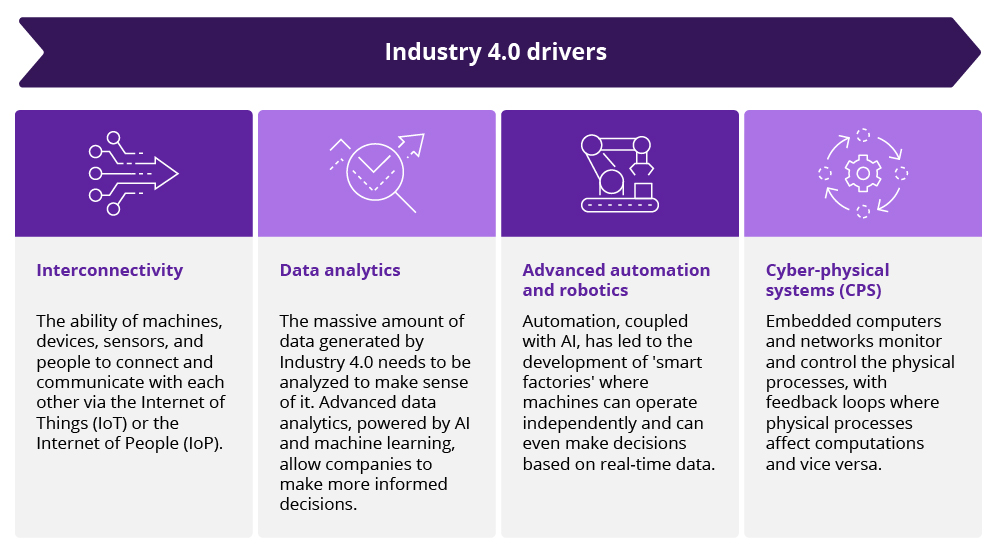
The transformative wave of the fourth industrial revolution, or Industry 4.0, is driven by a convergence of groundbreaking technologies. These technologies not only facilitate improved operational efficiency but also spur innovation, leading to the creation of new business models and opening up unprecedented opportunities.
Internet of Things (IoT). IoT consists of interconnected devices embedded with sensors and software. In Industry 4.0, IoT allows for real-time information flow, enabling precision and timeliness in decision-making processes.
Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI). AI and machine learning enable machines to learn from data autonomously, identify patterns and make decisions. These technologies foster productivity by enabling predictive maintenance, quality control and waste reduction.
Cloud and edge computing. Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources, while edge computing brings data storage and computation closer to the data source, reducing latency. Both offer the computational power and storage capacity needed for handling vast amounts of data.
Digital twins. A digital twin is a virtual model of a process, product or service. Serving as a bridge between the physical and digital worlds, digital twins enable data analysis and system monitoring, pre-empting problems before they occur.
IT-OT integration. The integration of information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) is critical in Industry 4.0. This convergence improves information flow, enables better real-time decision-making and enhances operational efficiency.
These technologies serve as the backbone of Industry 4.0, each contributing to a synergistic whole that is greater than the sum of its parts. Embracing these technologies can transform traditional manufacturing facilities into smart factories, where machines communicate with each other, operations are optimized based on real-time data and production processes become more flexible and efficient.
However, with this increased digitization and interconnectivity comes the challenge of cybersecurity.
The critical role of cybersecurity in Industry 4.0
Embracing the revolutionary wave of Industry 4.0, the manufacturing sector is experiencing a profound digital transformation. As interconnectivity and data sharing soar, protecting against cybersecurity threats becomes a critical task for all businesses. These threats may come in different forms, ranging from data breaches to disruptive service interruptions, carrying the potential to cause significant disruption in manufacturing processes.
With systems increasingly intertwined, the attack surface for cyber threats expands exponentially. Industry 4.0 relies heavily on data, demanding enhanced data protection policies to ensure the confidentiality of sensitive information.
Effectively tackling these cybersecurity challenges calls for a holistic approach:
- Risk assessment. The initial step is to evaluate cybersecurity risks in the current landscape. Conducting a meticulous risk assessment involves identifying system vulnerabilities and assessing the potential consequences if these vulnerabilities are exploited
- Implementing robust security measures. Strengthening system security involves adopting measures such as fortified firewalls, data encryption, regular system updates and continuous monitoring to detect anomalous activities
- Education programs for employees. Regular training and education programs are crucial for creating a cybersecurity-aware workforce. Equipping employees with essential knowledge of the best cybersecurity practices and the ability to identify and respond to potential threats in a timely manner reduces the risk of cyber incidents
- Introducing an incident response plan. Having a well-defined plan to identify and address cybersecurity incidents minimizes damage when breaches occur and facilitates swift recovery
Striking the right balance between harnessing the potential of emerging technologies and upholding cybersecurity will be pivotal in driving successful digital transformation in the manufacturing sector.
Embracing the future of Industry 4.0
In the modern software-defined environment, the fourth industrial revolution, also known as Industry 4.0, stands as a pivotal moment for the manufacturing industry. This technological revolution offers a myriad of advantages, including improved efficiency, increased flexibility, enhanced decision-making capabilities, and elevated customer satisfaction. These benefits have the power to accelerate business growth and generate positive outcomes for both customers and manufacturers.
Nevertheless, the path to fully embracing Industry 4.0 carries a set of challenges. Significant capital investments, technological compatibility issues, skill gaps, data privacy threats and security considerations all necessitate strategic recognition and resolution.
Essential technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, cloud and edge computing, digital twins, and the integration of IT and OT are the cornerstones of Industry 4.0, enabling the transformation of manufacturing processes and the foundation of smart factories.
Bridging the digital innovation gap entails more than just adopting new-age technologies. It requires cultivating a comprehensive digital culture — one that proactively engages with emerging technologies, establishes resilient cybersecurity measures, and, crucially, embraces a continuous willingness to adapt and learn within an ever-evolving digital landscape.